- The Data Integrity Scan for Crash Recovery is a task that doesn't show as a storage job, and there's no progress indicator. If the task is showing as running, it's running. When it completes, it shows completed. Also, you can view the status of a running schedule task by using this cmdlet:
Get-ScheduledTask | ? State -eq running Get-ClusterResource -Name "Physical Disk Resource Name" | Set-ClusterParameter DiskRunChkDsk 0 Stop-ClusterResource "Physical Disk Resource Name" Start-ClusterResource "Physical Disk Resource Name" Add-ClusterSharedVolume -Name "Physical Disk Resource Name" Use the Data Integrity Scan for Crash Recovery task to synchronize and clear a full dirty region tracking (DRT) log. This task can take several hours to complete. The Data Integrity Scan for Crash Recovery is a task that doesn't show as a storage job, and there's no progress indicator. If the task is showing as running, it's running. When it completes, it shows as completed. If you cancel the task or restart a node while this task is running, the task needs to start over from the beginning.
Event 5120 with STATUS_IO_TIMEOUT c00000b5
For Windows Server 2016: To reduce the chance of experiencing these symptoms while applying the update with the fix, we recommend you use the storage maintenance mode procedure to install the October 18, 2018, cumulative update for Windows Server 2016 or a later version when the nodes currently have installed a Windows Server 2016 cumulative update that was released from May 8, 2018 to October 9, 2018.
You might get event 5120 with STATUS_IO_TIMEOUT c00000b5 after you restart a node on Windows Server 2016 with cumulative update that was released from May 8, 2018 KB 4103723 to October 9, 2018 KB 4462917 installed.
When you restart the node, Event 5120 is logged in the System Event log and includes one of these error codes:
Event Source: Microsoft-Windows-FailoverClustering Event ID: 5120 Description: Cluster Shared Volume 'CSVName' ('Cluster Virtual Disk (CSVName)') has entered a paused state because of 'STATUS_IO_TIMEOUT(c00000b5)'. All I/O will temporarily be queued until a path to the volume is reestablished. Cluster Shared Volume 'CSVName' ('Cluster Virtual Disk (CSVName)') has entered a paused state because of 'STATUS_CONNECTION_DISCONNECTED(c000020c)'. All I/O will temporarily be queued until a path to the volume is reestablished. When an Event 5120 is logged, a live dump generates to collect debugging information that can cause other symptoms or affect performance. When the live dump generates, it causes a brief pause. The pause enables a snapshot of memory to write the dump file. Systems with a great amount of memory and under stress might cause nodes to drop out of cluster membership and cause the following Event 1135 to be logged.
Event source: Microsoft-Windows-FailoverClustering Event ID: 1135 Description: Cluster node 'NODENAME'was removed from the active failover cluster membership. The Cluster service on this node might have stopped. This could also be due to the node having lost communication with other active nodes in the failover cluster. Run the Validate a Configuration wizard to check your network configuration. If the condition persists, check for hardware or software errors related to the network adapters on this node. Also check for failures in any other network components to which the node is connected such as hubs, switches, or bridges. A change introduced in May 8, 2018 to Windows Server 2016 was a cumulative update to add SMB Resilient Handles for the Storage Spaces Direct intra-cluster SMB network sessions. This update was made to improve resiliency to transient network failures and improve how RoCE handles network congestion. These improvements also inadvertently increased timeouts when SMB connections try to reconnect and waits to time out when a node is restarted. These issues can affect a system that's under stress. During unplanned downtime, IO pauses up to 60 seconds have also been observed while the system waits for connections to time out. To fix this issue, install the October 18, 2018, cumulative update for Windows Server 2016 or a later version.
This update aligns the CSV time-outs with SMB connection time-outs to fix this issue. It doesn't implement the changes to disable live dump generation mentioned in the Workaround section.
Shutdown process flow
- Run the Get-VirtualDisk cmdlet, and make sure that the HealthStatus value is Healthy.
- Drain the node by running this cmdlet:
Suspend-ClusterNode -Drain Get-StorageFaultDomain -Type StorageScaleUnit | Where-Object "> | Enable-StorageMaintenanceMode Get-StorageFaultDomain -Type StorageScaleUnit | Where-Object "> | Disable-StorageMaintenanceMode Resume-ClusterNode Get-StorageJob Disabling live dumps
To mitigate the effects of live dump generation on systems with a great amount of memory and under stress, you can disable live dump generation. These three options are provided:
- Disable all dumps
- Allow only one LiveDump
- Disable cluster generation
This procedure can prevent the collection of diagnostic information that Microsoft Support might need to investigate this problem. A Support agent might ask you to re-enable live dump generation based on specific troubleshooting scenarios.
Disable all dumps
To completely disable all dumps, including live dumps system-wide, follow these steps. Use this procedure for this scenario:
- Create the following registry key: HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\CrashControl\ForceDumpsDisabled
- Under the new ForceDumpsDisabled key, create a REG_DWORD property as GuardedHost, and then set its value to 0x10000000.
- Apply the new registry key to each cluster node.
You must restart the computer for the nregistry change to take effect.
After this registry key is set, live dump creation will fail and generate a STATUS_NOT_SUPPORTED error.
Allow only one LiveDump
By default, Windows Error Reporting allows only one LiveDump per report type per seven days and only one LiveDump per machine per five days. You can change that by setting the following registry keys to only allow one LiveDump on the machine forever.
reg add "HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\Windows Error Reporting\FullLiveKernelReports" /v SystemThrottleThreshold /t REG_DWORD /d 0xFFFFFFFF /f reg add "HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\Windows Error Reporting\FullLiveKernelReports" /v ComponentThrottleThreshold /t REG_DWORD /d 0xFFFFFFFF /f You must restart the computer for the change to take effect.
Disable cluster generation
To disable cluster generation of live dumps (such as when an Event 5120 is logged), run this cmdlet:
(Get-Cluster).DumpPolicy = ((Get-Cluster).DumpPolicy -Band 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFE) This cmdlet has an immediate effect on all cluster nodes without a computer restart.
Slow IO performance
If you see slow IO performance, check if cache is enabled in your Storage Spaces Direct configuration.
There are two ways to check:
-
Use the cluster log. Open the cluster log with a text editor of your choice and search for "[=== SBL Disks ===]". You see a list of the disk on the node the log was generated on. Cache Enabled Disks Example: Notice that the state is CacheDiskStateInitializedAndBound and there's a GUID present here.
[=== SBL Disks ===] ,3,false,true,1,48,,CacheDiskStateInitializedAndBound,1,8087,54,false,false,HGST,HUH721010AL4200,7PG3N2ER,A21D,,[R/M 0 R/U 0 R/T 0 W/M 0 W/U 0 W/T 0], Cache Not Enabled: Here you can see that there's no GUID present and the state is CacheDiskStateNonHybrid .
[=== SBL Disks ===] ,12,false,true,1,24,,CacheDiskStateNonHybrid,0,0,0,false,false,HGST,HUH721010AL4200,7PGXXG6C,A21D,,[R/M 0 R/U 0 R/T 0 W/M 0 W/U 0 W/T 0], Cache Not Enabled: When all disks are of the same type, case isn't enabled by default. Here you can see there's no GUID present and the state is CacheDiskStateIneligibleDataPartition .
,10,false,false,1,20,,CacheDiskStateIneligibleDataPartition,0,0,0,false,false,NVMe,INTEL SSDPE7KX02,PHLF7330004V2P0LGN,0170,,[R/M 0 R/U 0 R/T 0 W/M 0 W/U 0 W/T 0], - Open the XML file by using "$d = Import-Clixml GetPhysicalDisk.XML".
- Run ipmo storage .
- Run $d . Notice that Usage is Auto-Select, not Journal.
You should see an output similar to this:
| FriendlyName | SerialNumber | MediaType | CanPool | OperationalStatus | HealthStatus | Usage | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NVMe INTEL SSDPE7KX02 | PHLF733000372P0LGN | SSD | False | OK | Healthy | Auto-Select | 1.82 TB |
| NVMe INTEL SSDPE7KX02 | PHLF7504008J2P0LGN | SSD | False | OK | Healthy | Auto-Select | 1.82 TB |
| NVMe INTEL SSDPE7KX02 | PHLF7504005F2P0LGN | SSD | False | OK | Healthy | Auto-Select | 1.82 TB |
| NVMe INTEL SSDPE7KX02 | PHLF7504002A2P0LGN | SSD | False | OK | Healthy | Auto-Select | 1.82 TB |
| NVMe INTEL SSDPE7KX02 | PHLF7504004T2P0LGN | SSD | False | OK | Healthy | Auto-Select | 1.82 TB |
| NVMe INTEL SSDPE7KX02 | PHLF7504002E2P0LGN | SSD | False | OK | Healthy | Auto-Select | 1.82 TB |
| NVMe INTEL SSDPE7KX02 | PHLF7330002Z2P0LGN | SSD | False | OK | Healthy | Auto-Select | 1.82 TB |
| NVMe INTEL SSDPE7KX02 | PHLF733000272P0LGN | SSD | False | OK | Healthy | Auto-Select | 1.82 TB |
| NVMe INTEL SSDPE7KX02 | PHLF7330001J2P0LGN | SSD | False | OK | Healthy | Auto-Select | 1.82 TB |
| NVMe INTEL SSDPE7KX02 | PHLF733000302P0LGN | SSD | False | OK | Healthy | Auto-Select | 1.82 TB |
| NVMe INTEL SSDPE7KX02 | PHLF7330004D2P0LGN | SSD | False | OK | Healthy | Auto-Select | 1.82 TB |
How to destroy an existing cluster so you can use the same disks again
In a Storage Spaces Direct cluster, disable Storage Spaces Direct and use the clean-up process described in Clean drives. The clustered storage pool still remains in an Offline state, and the Health Service is removed from cluster.
The next step is to remove the phantom storage pool:
Get-ClusterResource -Name "Cluster Pool 1" | Remove-ClusterResource Now, if you run Get-PhysicalDisk on any of the nodes, you see all the disks that were in the pool. For example, in a lab with a 4-Node cluster with 4 SAS disks, 100 GB each presented to each node. In that case, after Storage Space Direct is disabled, which removes the SBL (Storage Bus Layer) but leaves the filter, if you run Get-PhysicalDisk, it should report 4 disks excluding the local OS disk. Instead it reported 16. This behavior is the same for all nodes in the cluster. When you run a Get-Disk command, you see the locally attached disks numbered as 0, 1, 2, and so on, as seen in this sample output:
| Number | Friendly Name | Serial Number | HealthStatus | OperationalStatus | Total Size | Partition Style |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Msft Virtual | Healthy | Online | 127 GB | GPT | |
| Msft Virtual | Healthy | Offline | 100 GB | RAW | ||
| Msft Virtual | Healthy | Offline | 100 GB | RAW | ||
| Msft Virtual | Healthy | Offline | 100 GB | RAW | ||
| Msft Virtual | Healthy | Offline | 100 GB | RAW | ||
| 1 | Msft Virtual | Healthy | Offline | 100 GB | RAW | |
| Msft Virtual | Healthy | Offline | 100 GB | RAW | ||
| 2 | Msft Virtual | Healthy | Offline | 100 GB | RAW | |
| Msft Virtual | Healthy | Offline | 100 GB | RAW | ||
| Msft Virtual | Healthy | Offline | 100 GB | RAW | ||
| Msft Virtual | Healthy | Offline | 100 GB | RAW | ||
| Msft Virtual | Healthy | Offline | 100 GB | RAW | ||
| 4 | Msft Virtual | Healthy | Offline | 100 GB | RAW | |
| 3 | Msft Virtual | Healthy | Offline | 100 GB | RAW | |
| Msft Virtual | Healthy | Offline | 100 GB | RAW | ||
| Msft Virtual | Healthy | Offline | 100 GB | RAW | ||
| Msft Virtual | Healthy | Offline | 100 GB | RAW |
Error message about "unsupported media type" when you create a Storage Spaces Direct cluster by using Enable-ClusterS2D
You might see similar errors when you run the Enable-ClusterS2D cmdlet:
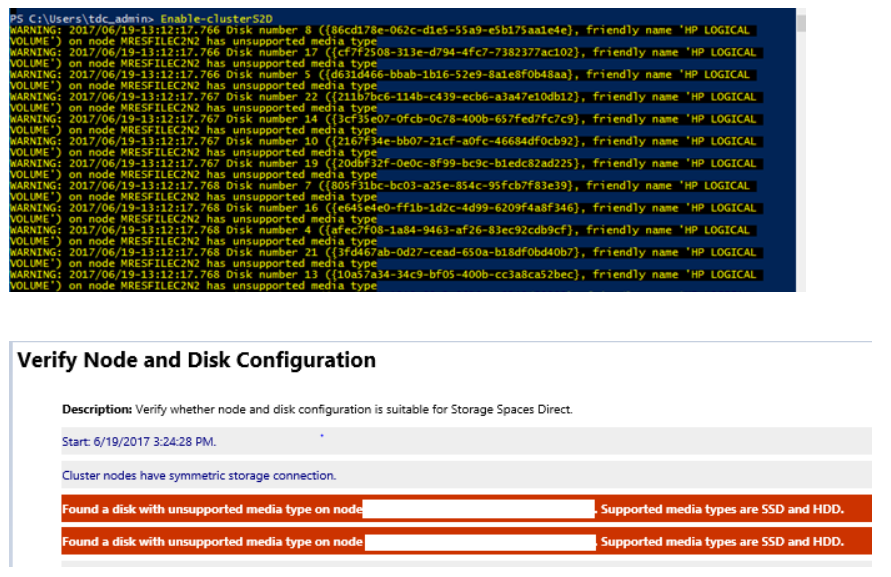
To fix this issue, ensure the HBA adapter is configured in HBA mode. No HBA should be configured in RAID mode.
Enable-ClusterStorageSpacesDirect hangs at 'Waiting until SBL disks are surfaced' or at 27%
You see the following information in the validation report:
Disk connected to node returned a SCSI Port Association and the corresponding enclosure device couldn't be found. The hardware isn't compatible with Storage Spaces Direct (S2D). Contact the hardware vendor to verify support for SCSI Enclosure Services (SES).
The issue is with the HPE SAS expander card that lies between the disks and the HBA card. The SAS expander creates a duplicate ID between the first drive connected to the expander and the expander itself. This issue has been resolved in HPE Smart Array Controllers SAS Expander Firmware: 4.02.
Intel SSD DC P4600 series has a nonunique NGUID
You might see an issue where an Intel SSD DC P4600 series device seems to be reporting similar 16-byte NGUID for multiple namespaces such as 0100000001000000E4D25C000014E214 or 0100000001000000E4D25C0000EEE214 in this example.
| UniqueId | DeviceId | MediaType | BusType | SerialNumber | Size | CanPool | FriendlyName | OperationalStatus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5000CCA251D12E30 | 0 | HDD | SAS | 7PKR197G | 10000831348736 | False | HGST | HUH721010AL4200 |
| eui.0100000001000000E4D25C000014E214 | 4 | SSD | NVMe | 0100_0000_0100_0000_E4D2_5C00_0014_E214. | 1600321314816 | True | INTEL | SSDPE2KE016T7 |
| eui.0100000001000000E4D25C000014E214 | 5 | SSD | NVMe | 0100_0000_0100_0000_E4D2_5C00_0014_E214. | 1600321314816 | True | INTEL | SSDPE2KE016T7 |
| eui.0100000001000000E4D25C0000EEE214 | 6 | SSD | NVMe | 0100_0000_0100_0000_E4D2_5C00_00EE_E214. | 1600321314816 | True | INTEL | SSDPE2KE016T7 |
| eui.0100000001000000E4D25C0000EEE214 | 7 | SSD | NVMe | 0100_0000_0100_0000_E4D2_5C00_00EE_E214. | 1600321314816 | True | INTEL | SSDPE2KE016T7 |
To fix this issue, update the firmware on the Intel drives to the latest version. Firmware version QDV101B1 from May 2018 is known to resolve this issue.
The May 2018 release of the Intel SSD Data Center Tool includes a firmware update, QDV101B1, for the Intel SSD DC P4600 series.
HealthStatus for the physical disk and OperationalStatus
In a Windows Server 2016 Storage Spaces Direct cluster, you might see the HealthStatus for one or more physical disks as Healthy, while the OperationalStatus is Removing from Pool, OK.
The Removing from Pool status is an intent set when Remove-PhysicalDisk is called but stored in Health to maintain state and allow recovery if the remove operation fails. You can manually change the OperationalStatus to Healthy with one of these methods:
- Remove the physical disk from the pool, and then add it back.
- Import-Module Clear-PhysicalDiskHealthData.ps1.
- Run the Clear-PhysicalDiskHealthData.ps1 script to clear the intent. This script is available for download as a .txt file. You must save it as a ps1 file before you can run it.
Here are some examples showing how to run the script:
-
Use the SerialNumber parameter to specify the disk you need to set to Healthy. You can get the serial number from WMI MSFT_PhysicalDisk or Get-PhysicalDisk . This example uses zeros to stand for the serial number.
Clear-PhysicalDiskHealthData -Intent -Policy -SerialNumber 000000000000000 -Verbose -Force Clear-PhysicalDiskHealthData -Intent -Policy -UniqueId 00000000000000000 -Verbose -Force File copy is slow
You might see that the file copy takes longer than expected when you use File Explorer to copy a large VHD to the virtual disk.
We don't recommend that you use File Explorer, Robocopy, or Xcopy to copy a large VHD to the virtual disk. It results in slower than expected performance. The copy process doesn't go through the Storage Spaces Direct stack, which sits lower on the storage stack, and instead acts like a local copy process.
If you want to test Storage Spaces Direct performance, we recommend you use VMFleet and Diskspd to load and stress test the servers to get a base line and set expectations of the Storage Spaces Direct performance.
Expected events that you would see on rest of the nodes during the reboot of a node
It's safe to ignore these events:
Event ID 205: Windows lost communication with physical disk . This can occur if a cable failed or was disconnected, or if the disk itself failed. Event ID 203: Windows lost communication with physical disk . This can occur if a cable failed or was disconnected, or if the disk itself failed. If you're running Azure VMs, you can ignore this event: Event ID 32: The driver detected that the device \Device\Harddisk5\DR5 has its write cache enabled. Data corruption might occur.
Slow performance or "Lost Communication", "IO Error", "Detached" or "No Redundancy" errors for deployments that use Intel P3x00 NVMe devices
We've identified a critical issue that affects some Storage Spaces Direct users who use hardware based on the Intel P3x00 family of NVM Express (NVMe) devices with firmware versions before "Maintenance Release 8".
Individual OEMs might have devices that are based on the Intel P3x00 family of NVMe devices with unique firmware version strings. Contact your OEM for more information of the latest firmware version.
If you use hardware in your deployment based on the Intel P3x00 family of NVMe devices, we recommend that you immediately apply the latest available firmware (at least Maintenance Release 8).