

In the world of business, think of invoices like the superheroes of money matters. They’re not just papers or digital files; they’re the heartbeat of how businesses handle cash. Today, let’s talk about two important invoice heroes: Commercial Invoices and Tax Invoices.
Commercial Invoices are like friendly guides in a trade journey, showing what’s bought or sold. Now, Tax Invoices are a bit like financial superheroes, especially for taxes. They prove we’ve paid our dues.
These documents aren’t just boring papers – they’re like business superheroes, making sure everything is clear and legal. So, if you’re a business owner, an accountant, or someone dealing with a company’s money matters, get ready to understand these money superheroes!
A Commercial Invoice is a document that details the sale of goods between a seller and a buyer. Think of it as a friendly handshake between businesses, outlining the products or services provided and their respective costs. It is an essential record for both parties, aiding in smooth transactions and keeping things transparent.
These features collectively serve as the backbone of the Commercial Invoice, ensuring that every party involved in the transaction understands and agrees upon the crucial details.
Buyer and Seller Information
Names and addresses of both the buyer and the seller are prominently featured.
Goods or Services Description
Clearly outlines a description of the goods or services being bought or sold.
Quantity
Specifies the quantity of the products or the extent of the services involved in the transaction.
Price
Clearly states the price associated with each unit of the product or service.
Payment Terms
Outlines the agreed-upon terms for payment, including any deadlines or
installment details.
These simple points below highlight how Commercial Invoices are like magical tickets that help products cross borders effortlessly in the world of international trade.
International Significance
Commercial Invoices become even more important when businesses engage in international trade.
Customs Assessment
Customs officials rely on Commercial Invoices to figure out the duties and taxes applicable to imported goods.
Passports for Products
Think of Commercial Invoices as passports for products – they help goods move smoothly across borders.
Seamless Border Journey
A well-prepared Commercial Invoice ensures that products can travel hassle-free between countries.
Business’s Best Travel Companion
In international transactions, a properly filled-out Commercial Invoice is like the perfect travel companion for your business, making sure everything arrives at its destination without a hitch.

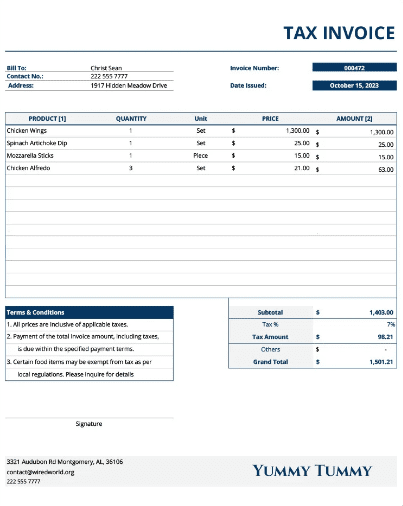
A Tax Invoice is a document issued by a seller to a buyer, just like a Commercial Invoice. However, its primary purpose is to serve as proof for the payment of taxes. It’s not just about the products; it’s about ensuring that the taxman gets his due.
These simple points outline the key requirements of a Tax Invoice, emphasizing the clarity and transparency it brings to financial dealings, particularly in the realm of taxes.
Seller and Buyer Information
Clearly mentions the names and addresses of both the seller and the buyer.
Unique Invoice Number
Assigns a distinctive invoice number to track and identify each transaction uniquely.
Date of Issue
Specifies the date when the Tax Invoice is created, ensuring a chronological record.
Description of Goods or Services
Provides a clear and detailed description of the goods or services involved in the transaction.
Inclusion of Applicable Taxes
Stands out as a crucial feature, highlighting the incorporation of taxes relevant to the transaction.
Transparency in Tax Transactions
The Tax Invoice ensures a transparent financial picture, especially regarding tax obligations.
Prevents Confusion
By including taxes in the invoice, it eliminates any confusion and establishes a straightforward understanding of the financial transaction.
Tax Invoices come into play when businesses need to account for taxes in their financial records. It’s not just about selling goods; it’s about fulfilling your tax obligations. Typically, businesses use Tax Invoices for transactions that involve the exchange of taxable goods or services.
Now, let’s draw a side-by-side comparison between Commercial and Tax Invoices to understand their distinct purposes.
Both Commercial and Tax Invoices feature details about the buyer, seller, and the exchanged products or services.
Commercial Invoices contribute to a business’s financial records, showcasing its revenue and expenses. Tax Invoices, on the other hand, directly impact tax calculations, ensuring that businesses adhere to tax regulations and report accurate figures.
Adopting these best practices ensures that businesses efficiently manage both Commercial and Tax Invoices, promoting accuracy, compliance, and overall financial health.
Ensure a clear understanding of the differences between Commercial and Tax Invoices to use them appropriately.
Maintain accurate and detailed documentation for each transaction, adhering to the specific requirements of each invoice type.
Keep abreast of tax regulations and updates to ensure Tax Invoices comply with the latest legal standards.
Establish a consistent record-keeping system for both Commercial and Tax Invoices to facilitate easy retrieval and reference.
Employ reliable invoicing software to streamline the creation and management of invoices, reducing the risk of errors.
Provide training to staff involved in the invoicing process, ensuring they understand the nuances of both Commercial and Tax Invoices.
Issue invoices promptly to maintain a smooth cash flow and meet regulatory deadlines, especially in the case of Tax Invoices.
Conduct regular audits to cross-check and ensure that all invoices align with business practices and legal requirements.
Seek advice from financial experts or tax professionals when in doubt, ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Communicate clearly with both internal and external stakeholders about invoicing procedures, reducing misunderstandings.
In conclusion, Commercial and Tax Invoices are vital instruments in the business orchestra. They each have distinct roles, contributing to the harmonious flow of financial transactions and ensuring businesses operate within the bounds of legality and transparency.
1. What are the penalties for using the wrong type of invoice?
Using the wrong invoice type may lead to financial consequences and legal issues. Penalties can include fines, audits, and potential disputes. It’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the correct invoicing practices to avoid such repercussions.
2. Can a commercial invoice be used for tax purposes?
No, a commercial invoice is not designed for tax purposes. While it records the sale of goods or services, it lacks the essential tax details. To fulfill tax obligations, use a dedicated tax invoice, ensuring transparency and compliance with tax regulations.
3. How do I know if I need to issue a tax invoice?
You typically need to issue a tax invoice when providing taxable goods or services. If your business is registered for VAT or other relevant taxes, issuing a tax invoice is necessary. Consult tax regulations or seek advice from a financial professional to determine your specific obligations.
4. What information is crucial in a tax invoice?
A tax invoice must include essential details such as the seller’s and buyer’s names and addresses, a unique invoice number, the date of issue, a clear description of goods or services, and the applicable taxes. Including this information ensures compliance and transparency in tax transactions.
5. Can I correct errors on an issued tax invoice?
Yes, you can correct errors on a tax invoice. However, it’s crucial to follow the guidelines provided by tax authorities. Generally, corrections should be made promptly, and a revised invoice should be issued to maintain accurate records and comply with tax regulations.